|
Alum
Alum mordant that is used for mordanting textiles when dyeing with natural dyes, is usually potassium alum (see below) but potassium alum is only one of very many different types of alums. Most of these are not suitable for use as mordants.
Alums are double sulfates of sodium, potassium, ammonium and several other cations combined with a metal ion such as aluminium, iron (and many others). For further information see the Wikipedia article on alums.
Calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a common substance found in rock all over the world, and is the main component of shells of marine organisms, pearls, snails and in eggshells. It is found in aragonite, calcite, chalk, limestone and marble and its chemical formula is CaCO3. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is the principal cause of hard water. It is commonly used as a dietary calcium supplement or as an antacid.
Chalk
Chalk is often used as a synonym for calcium carbonate but be careful when buying chalk for dyeing as the name may also be used for several other substances which are not effective for dyeing. The chalk sold in outdoor shops for rock climbing (magnesium carbonate) is not suitable and neither is school board chalk (calcium sulphate) or agricultural lime (calcium hydroxide).
|
|
|
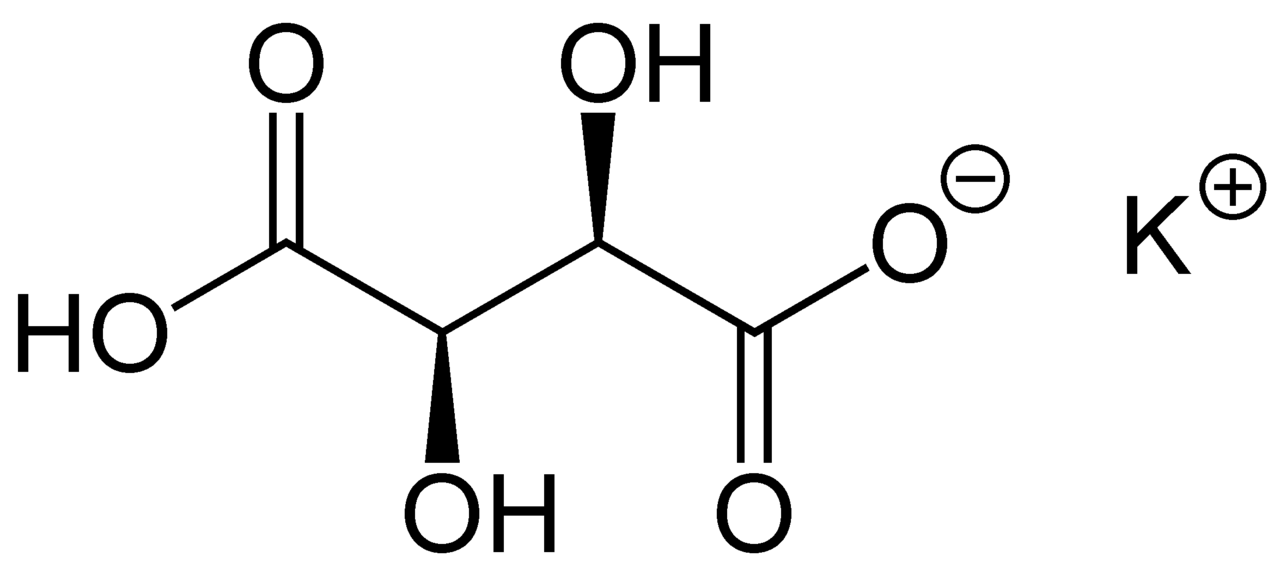
potassium bitartrate
|
|
Cream of tartar
Cream of tartar, or potassium bitartrate, is a white crystalline powder (also known as potassium hydrogen tartrate, potassium acid tartrate, and monopotassium tartrate) and has the formula KC4H5O6. It is a by-product of winemaking and is the potassium acid salt of tartaric acid.
Don’t buy cream of tartar sold for baking unless it is clearly labelled potassium bitartrate, as it is often a cream of tartar substitute that is not effective in dyeing (often sodium pyrophosphate).
Dithionite (see Sodium dithionite)
FFP1 & FFP2 dust masks or face masks, see the FAQ
Hydros (See Sodium dithionite)
Potassium alum
Potassium alum or alum mordant (also called potash alum or potassium aluminium sulfate) is the potassium double sulfate of aluminium. Its chemical formula is KAl(SO4)2 and it is commonly found in its dodecahydrate (i.e. 12 molecules of water) form as KAl(SO4)2·12(H2O). It is commonly used in water purification, leather tanning, fireproofing textiles and in baking powder as well as a mordant for dyeing textiles.
Sodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite (also known as Hydros, sodium hydrosulphite or sodium hydrosulfite) is a white crystalline powder with a weak sulphurous odour. It is stable under most conditions but decomposes in hot water and acid solutions.
Sodium dithionite is a water-soluble salt, and can be used as a reducing agent in aqueous solutions. It is used in some industrial dyeing processes, where a water-insoluble dye can be reduced to a water-soluble alkali metal salt. The reduction properties of sodium dithionite eliminate excess dye, residual oxide, and unintended pigments, thereby improving overall colour quality.
It can also be used for water treatment, gas purification, cleaning, and stripping and it is used in industrial processes as a sulphonating agent or a sodium ion source. In addition to the textile industry, sodium dithionite is used in industries concerned with leather, foods, polymers, photography, and many others due to its low toxicity and its wide range of applications.
Sodium dithionite is widely used in Europe as a safe alternative to spectralite for chemical dyeing with woad & indigo. You can substitute sodium dithionite where spectralite is mentioned in the text but you will need to double the quantities because sodium dithionite is not as strong.
Sodium hydrosulfite (is Sodium dithionite)
|
|
|
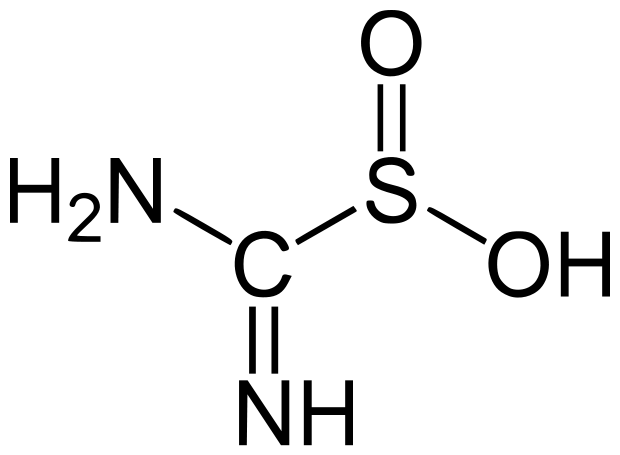
Spectralite or thiox
|
|
Spectralite (thiox or thiourea dioxide)
Spectralite is a reducing agent in aqueous solutions, like dithionite. It is often used as a reducing agent in woad vats and other indigo vats, removing oxygen for chemical dyeing techniques.
Sulfate is the American spelling of sulphate. They are the same thing.
Sulphate is the British spelling of sulfate. They are the same thing…
Thiox or thiourea dioxide is Spectralite.
Top of page
|